
#MetaHash, you can found online at https://metahash.org/, is a next-generation network based on the Blockchain 4.0 technology for sharing digital assets and a platform for creating and managing decentralized apps and services in real-time. The company was founded in 2018, with the majority of its executives located in Russia.
#MetaHash as a product has four distinct divisions, though all are interconnected and built on cryptocurrency and blockchain technology. They are:
1. TraceChain
The MetaHash blockchain. This cryptographic ledger supposedly has the ability to validate transactions in three seconds or less and has a capability in excess of five billion transactions per day.
2. MetaApps
A so-called new generation of DApps built by advanced smart contracts. MetaHash claims these are “real time” applications that can be developed with the help of literally any programming language.
3. MetaGate:
A “decentralized” version of the internet. MetaGate is both a directory for DApps – allowing access to them directly – and a multi-use digital wallet for several different cryptocurrencies.
4. MetaHashCoin (MHC):
The blockchain’s cryptocurrency. MHC is to be used as not just transactions and payments but also for data storage, powering DApps, and having those DApps listed on MetaGate directories.
In limited way, in this article, I will only give a brief review about #MetaHash's new blockchain generation, #TraceChain.
BLOCKCHAIN TECHNOLOGY
Plenty of startups are now using blockchain for everything, from music sharing to global payments, from monitoring diamond sales to the legalized marijuana industry. This is why the technology has a vast potential. When it comes to digital transactions and assets, you can place anything on the blockchain.
Blockchain is basically a distributed database that keeps shared records. These records are blocks, and every block of encrypted code has a record of the block history before it. Each block includes time-stamped information on the transactions made down to the second. The effect is a chain of those blocks to get them together; hence, its name.
A blockchain has two major components: an immutable ledger that the network keeps, and a decentralized network verifying and facilitating transactions. Everyone with access to the network could see this shared transaction data, but there is no possibility that the records can be corrupted or hacked. This decentralized trust means there is no one organization that controls the data, be it a tech giant or a big financial institution.
THE IDEA BEHIND #TraceChain
#TraceChain is currently the first fully functioning system based on decentralized distributed data register technology that changes technical principals used in all existing blockchain systems. The initiators behind the launch of the Blockchain 2.0 system are former game developers Gleb Nikitin and Anton Agranovsky (you can check #MetaHash team members at https://metahash.org/).
#MetaHash believes that all existing blockchain systems are too slow
and too expensive or are not fully
decentralized. The company took several cases as a comparative analysis of the systems that currently hold leading positions in the market, as it stated on its whitepaper (https://metahash.org/docs/MetaHash_WhitePaper_EN.pdf), to support the statements.
1. Bitcoin
Bitcoin's PoW (Proof of Work), as example, it is a reliable, but very expensive, network integrity protection mechanism. The synchronization process in blockchain is also renowned for the problem of slow nodes. The network is slow as long as its nodes are slow.
2. Ethereum
Ethereum features a good implementation of PoW, but at a very slow speed caused by direct synchronization between a multitude of participants and low throughput of many PoW nodes.
Its smart contracts are of particular value because they enable response to events in the Ethereum network, but unfortunately they cannot react to anything else and are unsuitable for real-time applications.
3. EOS
EOS is a reliable and fast banking system. However, it is centralized. 20 supercomputers control the network and provide a maximum number of votes. These top 20 computers synchronize transaction data and receive all commissions. Sometimes the commission is paid to one more computer which is chosen on the basis of the weight of votes cast in its favor.

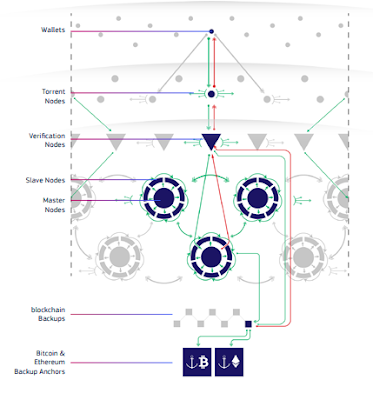
#TraceChain TECHNOLOGY
#TraceChain is the new internet protocol that the #MetaHash network is based on. #TraceChain uses a mathematical model of optimal signal propagation across the network. The synchronization of thousands of computers overloads a network and slows it down. To solve this issue, #TraceChain relies on mathematical algorithms powered by #TraceChain AI - all signals go from the outer radius to the cores. The signals are synchronized in multiple powerful cores and go back across the network.
The more computers that need to be simultaneously synchronized, the higher the load on the network. The cores are not static and are constantly altered by voting. Adding high-performance computers to the network does not automatically make them cores, which protects the network against attacks. The core's segments are fully decentralized and protected by Trust algorithms and additional verifications. The performance of the network core's segments is checked and protected by external radius.

HOW #TraceChain TECHNOLOGY WORKS?
#MetaHash created not just a new variation of a blockchain, but to approach the problem from an different angle. #MetaHash developers tried to maximize the synchronization speed of distributed computer networks, instead of improving the protocol. After multiple tests made, #MetaHash obtained multi-layered architecture, with the external radius keeping connection with multiple clients, the medium radius bearing the load of slow intercontinental connections and the central parts being responsible for the full synchronization of the lost transactions. In fact, the data uses multiple weak internet channels to reach computers using the fastest ones, ensures they’re synchronized and then comes back to the network. The new synchronization speed enables implementation of a new type of consensus multi-PoS, with all computers on the network simultaneously verifying the accuracy of every transaction and of each other’s work.
The principle of intercontinental data transfer deserves special attention. Usually, this process greatly slows down the synchronization of computer networks. In #TraceChain, the machine learning (AI) allows for the creation of a network map. Thereafter, all accessible small channels are used to deliver the incoming transactions to the next well-interconnected group of computers.
Having optimized the principle of synchronization of the distributed computer networks, #MetaHash managed to reach a synchronization speed that allows the entire network to jointly verify every transaction made by the users. Unlike a classic blockchain, a block is created by the vote of many machines at the same time and is validated by the network as a whole and not by different computers voting in turn. If a computer is not fast enough to approve all the transactions in the block, it will validate only the part that it can. However, all weak computers join together to validate every transaction many times. The algorithm of the consensus used in #MetaHash became known as multi-PoS, meaning that many computers confirm or decline every transaction simultaneously, and the network is protected by network coins, limited in number, that can be obtained only during the initial coin offering or, in future, by participating in validation of the transactions.
About Author:
BITCOINTALK USERNAME: tpq01349
BITCOINTALK PROFILE LINK: HERE
ETH ADDRESS: 0xA73fA2565C18218AC6510c8CD3B220F5794f3B84


Happy to found this blog. I have some facts related to this blog and I would like to share with all its readers. Definitely it is going to help everyone and aware people with some more knowledgeable points
ReplyDeletebest live streaming company in india